The most prominent feature of the frequency response of a resonant circuit is a sharp resonant peak in its amplitude characteristics.
Define resonant frequency of a circuit.
If the supply frequency is changed the value of x l 2πfl and x c 1 2πfc is also changed.
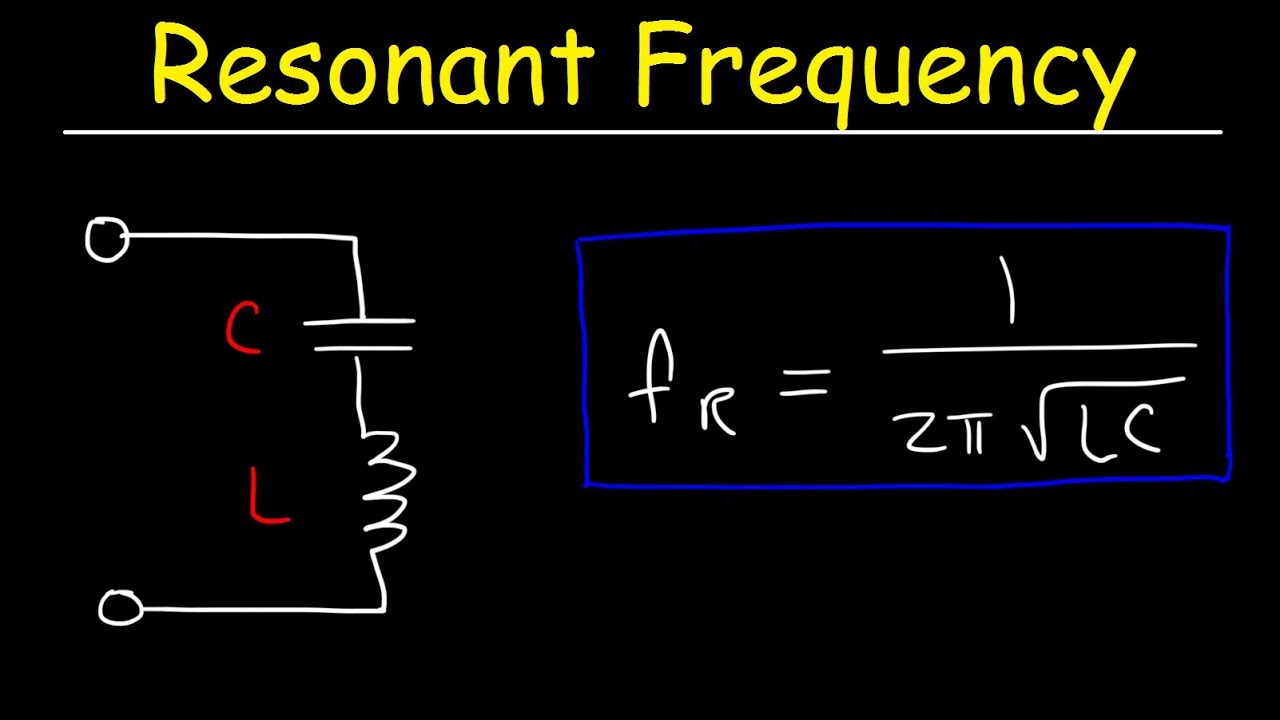
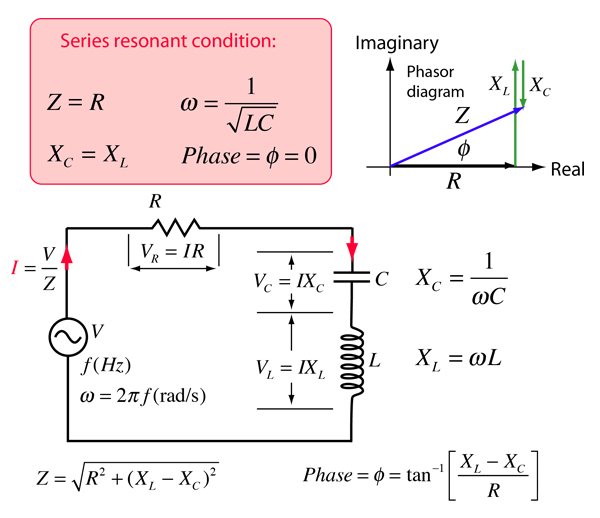
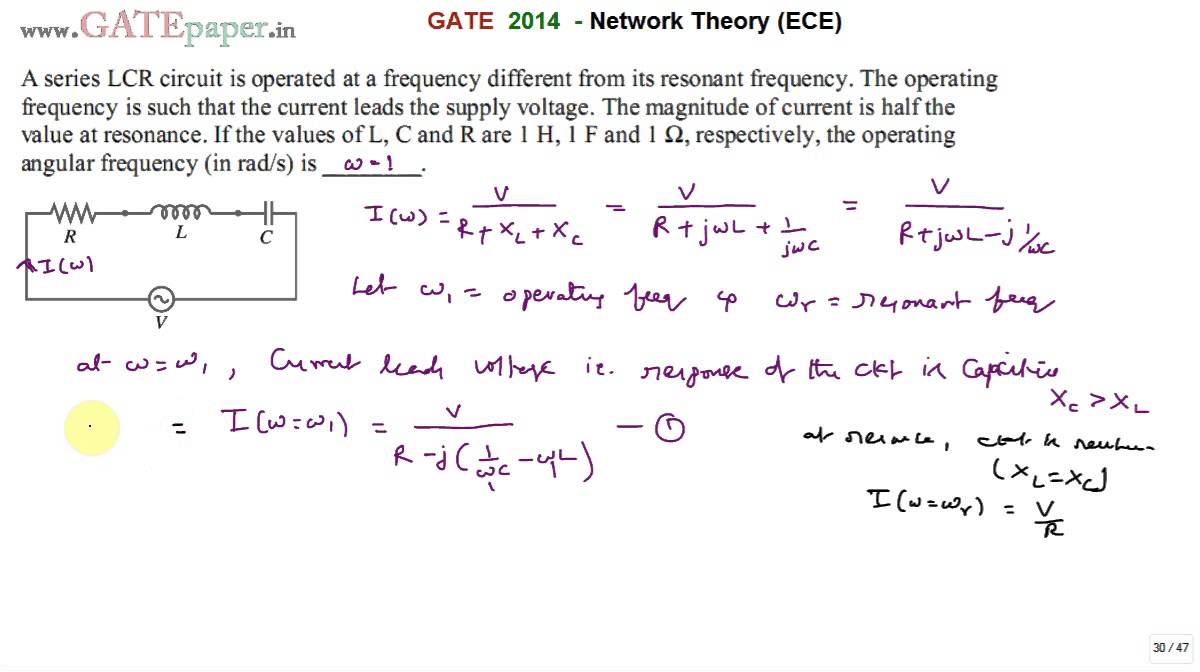
Resonant frequency the resonant frequency condition arises in the series circuit when the inductive reactance is equal to the capacitive reactance.
Electrical resonance occurs in an electric circuit at a particular resonant frequency when the impedances or admittances of circuit elements cancel each other.
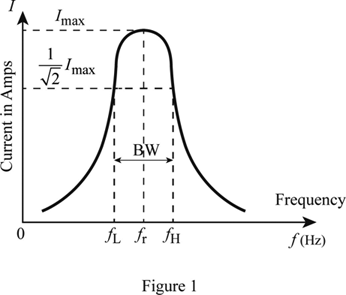
The peak resonance frequency on the other hand depends on the value of the resistor and is described as the damped resonant frequency.
The resonant frequency for an rlc circuit is the same as a circuit in which there is no damping hence undamped resonance frequency.
Resonant circuits exhibit ringing and can generate higher voltages and currents.
Resonant circuit synonyms resonant circuit pronunciation resonant circuit translation english dictionary definition of resonant circuit.
However its high current and very high component voltage values can cause damage to the circuit.
The q of an inductor with a series loss resistance is the q of a resonant circuit using that inductor including its series loss and a perfect capacitor.
Parallel resonance which is more common in electronic practice requires a more careful definition.
An lc circuit also called a resonant circuit tank circuit or tuned circuit is an electric circuit consisting of an inductor represented by the letter l and a capacitor represented by the letter c connected together the circuit can act as an electrical resonator an electrical analogue of a tuning fork storing energy oscillating at the circuit s resonant frequency.
An electric circuit with inductance and capacitance chosen to allow the greatest flow of current at a certain frequency.
A parallel circuit containing a resistance r an inductance l and a capacitance c will produce a parallel resonance also called anti resonance circuit when the resultant current through the parallel combination is in phase with the supply voltage.
Series resonance circuits are useful for constructing highly frequency selective filters.
The q of an individual reactive component depends on the frequency at which it is evaluated which is typically the resonant frequency of the circuit that it is used in.
A highly damped circuit will fail to resonate at all when not driven.
At resonance there will be a large circulating current between the inductor and the capacitor due to the energy of the oscillations then.