Basalt the once molten rock that makes up most new oceanic crust is a fairly magnetic substance and scientists began using magnetometers to measure the magnetism of the ocean floor in the 1950s what they discovered was that the magnetism of the ocean floor around.
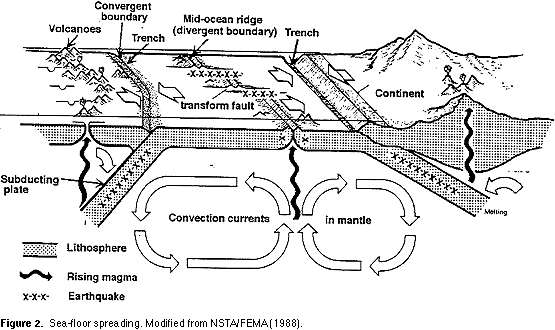
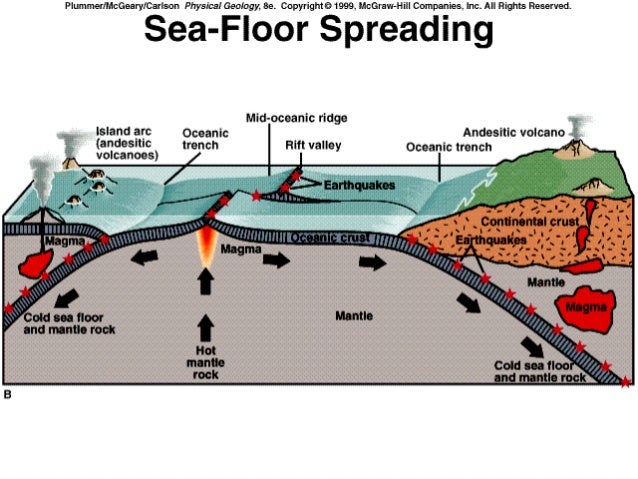
Diagram of ocean floor spreading connected by tranform.
The magnetism of mid ocean ridges helped scientists first identify the process of seafloor spreading in the early 20th century.
The lack of weathering and erosion in most areas however allows geological processes to be seen more clearly on.
Spreading rate is the rate at which an ocean basin widens due to seafloor spreading.
Mountains plains channels canyons exposed rocks and sediment covered areas.
Most such faults are found in oceanic crust where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of divergent boundaries forming a zigzag.
These age data also allow the rate of seafloor spreading to be determined and they show that rates.
This spreading creates a successively younger ocean floor and the flow of material is thought to bring about the migration or drifting apart of the continents.
The rate at which new oceanic lithosphere is added to each tectonic plate on either side of a mid ocean ridge is the spreading half rate and is equal to half of the spreading rate.
A transform fault or transform boundary is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal.
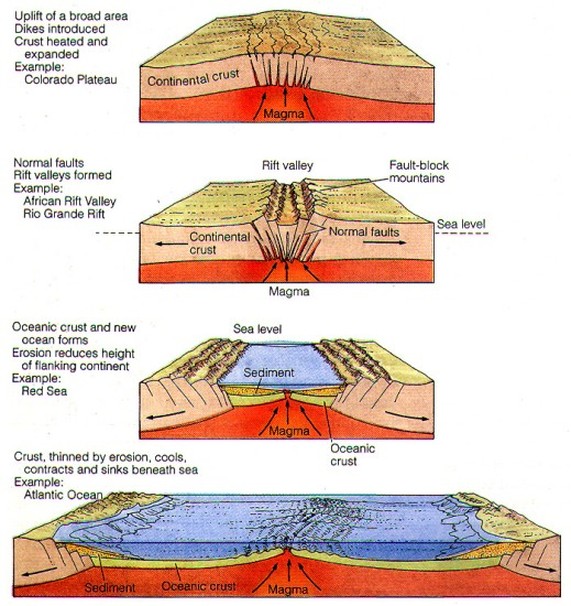
A divergent boundary occurs when two tectonic plates move away from each other.
Along these boundaries earthquakes are common and magma molten.
Spreading rates determine if the ridge is fast intermediate or slow.
Thus for fast spreading centers the ridge stands at higher elevations than for slow spreading centers.
The following features are shown at example depths to scale though each feature has a considerable range at which it may occur.
As upwelling of magma continues the plates continue to diverge a process known as seafloor spreading samples collected from the ocean floor show that the age of oceanic crust increases with distance from the spreading centre important evidence in favour of this process.
It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary either another transform a spreading ridge or a subduction zone.
If the spreading rate relative velocity is high magma must be rising rapidly and the lithosphere is relatively hot beneath the ridge.
Continental shelf 300 feet continental slope 300 10 000 feet abyssal plain 10 000 feet abyssal hill 3 000 feet up from the abyssal plain seamount 6 000 feet.
Sea floor topography is controlled by the age of the oceanic lithosphere and the rate of spreading.
A transform fault may occur in the portion of a fracture zone that exists between different offset spreading centres or that connects spreading centres to deep sea trenches in.
Exploration of the seafloor and the earth s crust.
The ocean floor has the same general character as the land areas of the world.
The continents bordering the atlantic ocean for example are believed to be moving away from the mid atlantic ridge at a rate of 1 2 cm 0 4 0 8 inch per year thus increasing.
Transform fault in geology and oceanography a type of fault in which two tectonic plates slide past one another.