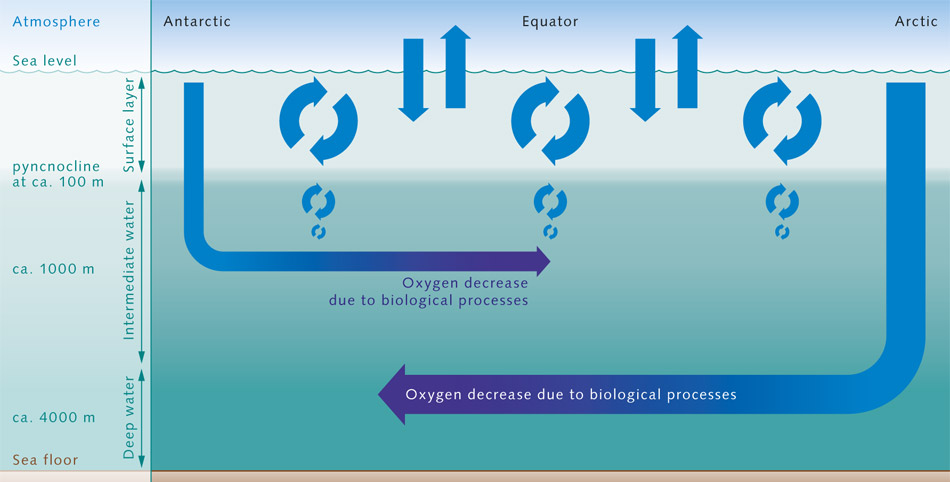
First melting sea ice increases the rate that the ocean mixes which dredges up co 2 rich deep ocean waters.
Dissolved carbon dioxide in water on the ocean floor.
That also means the water at the bottom of the ocean like the water at the top is getting more acidic.
Consequently more co2 is being absorbed by the oceans altering the carbonate chemistry of ocean surface waters.
Carbonate compensation depth ccd is the depth in the oceans below which the rate of supply of calcite calcium carbonate lags behind the rate of solvation such that no calcite is preserved.
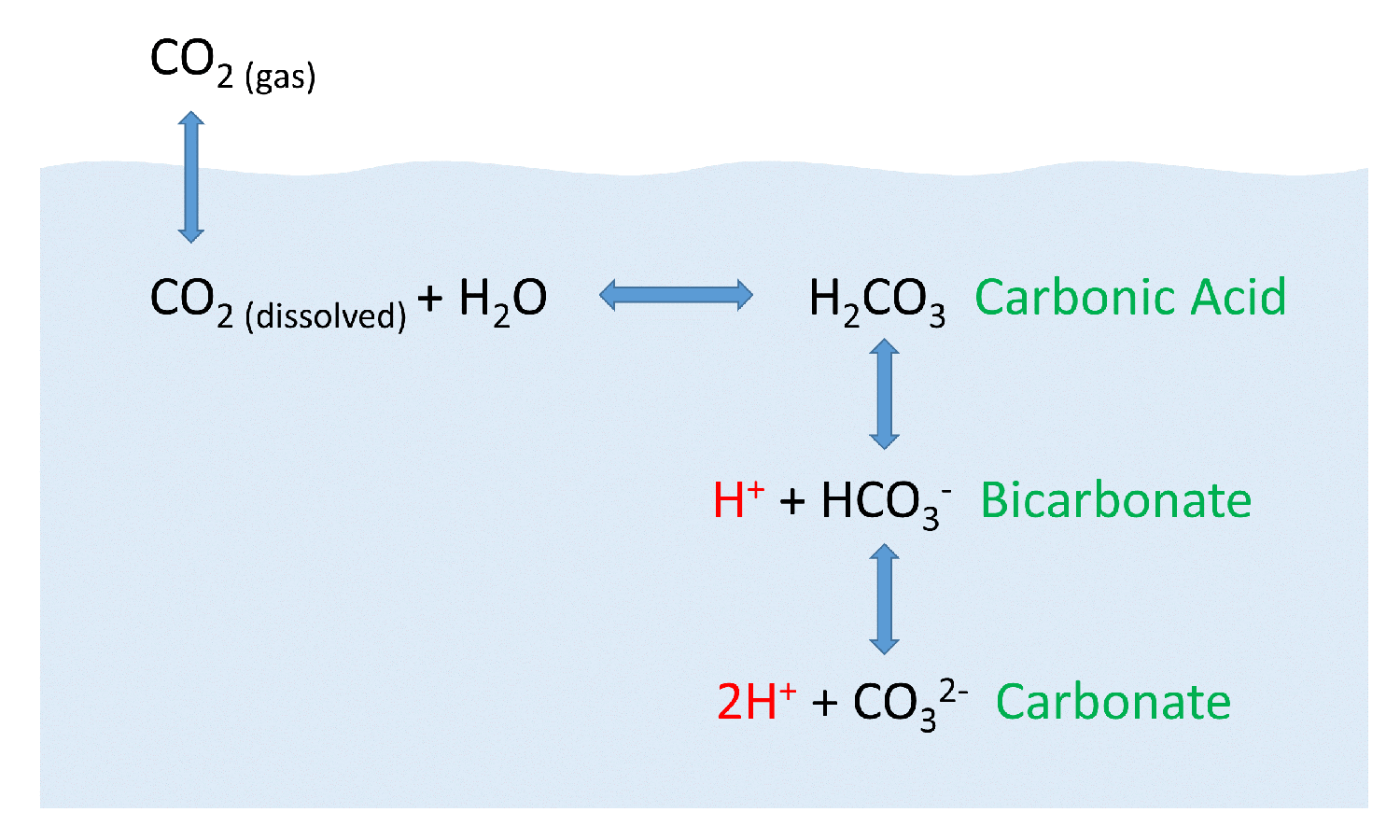
When co 2 is absorbed by seawater a series of chemical reactions occur resulting.
Since the beginning of industrialisation in the 18th century man made co2 emissions have progressively increased co2 concentrations in the atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide released from ocean floor triggered warming claims study researchers at the university of southampton studied fossilised plankton they found acidity in ocean surface water soared.
Excess carbon dioxide reaching the deep ocean means that the natural system can t keep up and the stores of calcium carbonate on the seafloor are dissolving.
After atmospheric carbon dioxide dissolves into the ocean the aqueous carbon dioxide reacts with seawater to form carbonic acid.
As carbonic acid continues to interact with water molecules carbonate is formed which increases the concentration of hydrogen ions in the ocean and consequently reduces ocean ph therefore increasing carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere decreases ocean ph.
Photosynthesis by tiny marine plants phytoplankton in the sunlit surface waters turns the carbon into organic matter.
Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere dissolves in the surface waters of the ocean.
Wind driven turbulence maintains the mixed layer by stirring the water near the ocean s surface.
Aragonite is more soluble than calcite so the aragonite compensation depth is generally.
Aragonite compensation depth hence acd describes the same behaviour in reference to aragonitic carbonates.
In the short term the ocean absorbs atmospheric carbon dioxide into the mixed layer a thin layer of water with nearly uniform temperature salinity and dissolved gases.
The ocean absorbs about 30 of the carbon dioxide co 2 that is released in the atmosphere as levels of atmospheric co 2 increase from human activity such as burning fossil fuels e g car emissions and changing land use e g deforestation the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the ocean also increases.